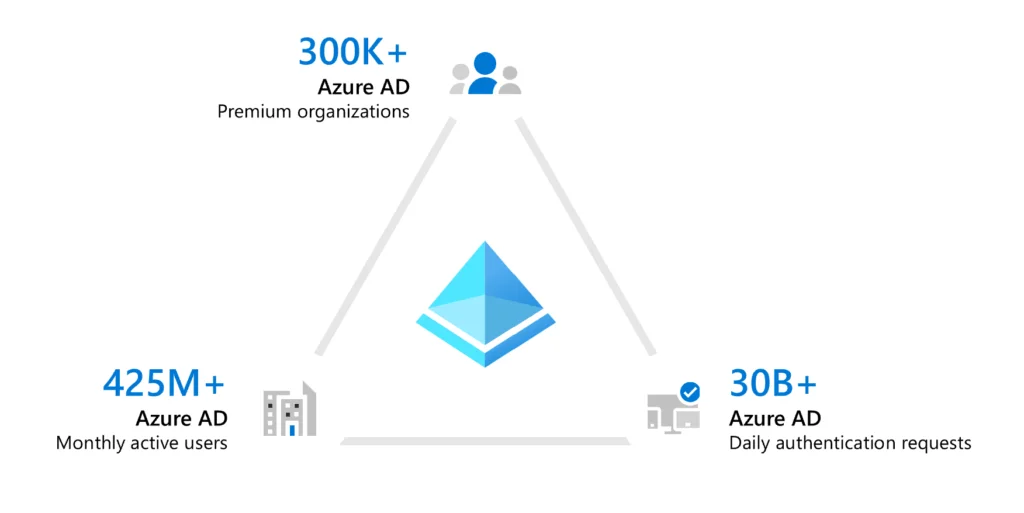
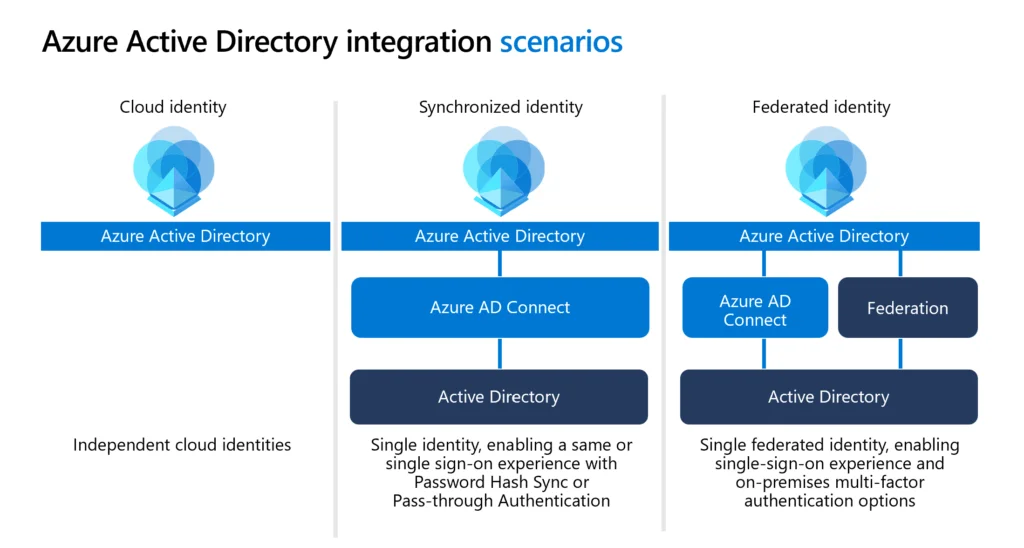
Azure Active Directory, a service for identity and access management for Microsoft’s cloud-based services, is an application used for user and identity management and authorization for all services and applications in IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS structures serving in the Microsoft Azure cloud.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): A type of service that primarily offers storage and network resources to organizations. Each product is offered as a separate service and is billed according to its usage.
PaaS (Platform as a Service): A cloud system entirely aimed at development and deployment, assisting in distributing all cloud-based applications you can think of. Like the IaaS service, it operates on a pay-as-you-go basis.
SaaS (Software as a Service): This service enables users to connect to and use web-based applications over the web. Examples include Teams, Outlook, Calendar (Microsoft Office 365). This application is accessed over the web and, like the other two services, is also pay-as-you-go.